Introduction
Valve manifolds are essential components in fluid control systems, widely used in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment. This article will cover the definition, structure, types, applications, advantages, and maintenance of valve manifolds.
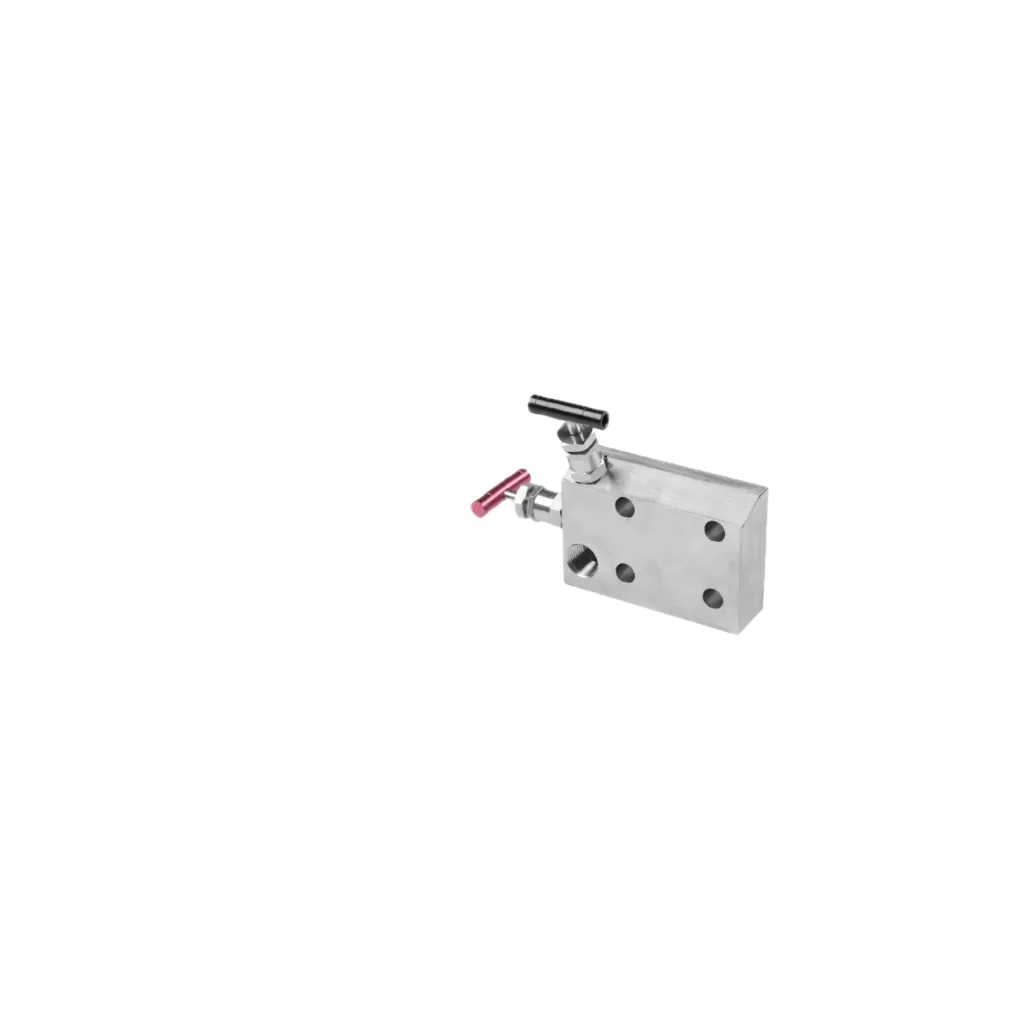
Definition
A valve manifold is an assembly that integrates multiple valves into a single unit, allowing for the efficient control of fluid flow direction, pressure, and flow rate. It streamlines the management of fluid systems and enhances operational efficiency.
Structure
The basic structure of a valve manifold includes:
Valves: Typically consists of ball valves, gate valves, or globe valves, which control the flow of fluid.
Connecting tubes: These connect the valves to other equipment or pipelines, ensuring smooth fluid movement.
Seals: Prevent leakage between valves and pipes, ensuring a secure connection.
Supports and Bases: Provide stability and support for the manifold assembly.
Types
Valve manifolds can be categorized into several types based on their design and application:
Single-stage Manifolds: Contains a single set of valves, suitable for simple fluid control.
Multi-stage Manifolds: Houses multiple sets of valves, ideal for complex fluid systems.
Electric Manifolds: Equipped with electric valves for automated control.
Pneumatic Manifolds: Utilizes pneumatic valves, suitable for gas control.
Applications
Valve manifolds have a wide range of applications, including:
Oil and Gas Industry: Manage the distribution and flow of oil and gas.
Chemical Industry: Control the transport and reaction of chemicals.
Water Treatment: Regulate the flow in water treatment processes.
HVAC Systems: Manage fluid flow in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
Advantages
The advantages of using valve manifolds include:
Space Efficiency: Integrating multiple valves reduces installation space.
Increased Efficiency: Simplified piping layout lowers fluid resistance.
Ease of Maintenance: Centralized management makes inspections and maintenance easier.
Enhanced Safety: Proper design minimizes the risk of leaks and failures.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the proper functioning of valve manifolds. Maintenance practices include:
Regular Inspections: Check the seals and valves for leaks to prevent fluid loss.
Cleaning: Periodically clean valves and pipes to prevent blockages from debris.
Lubrication: Lubricate moving parts to ensure smooth operation.
Replacement of Damaged Parts: Promptly replace worn or damaged valves and seals.
Conclusion
Valve manifolds play a vital role in modern industrial applications. By integrating multiple valves, they improve fluid control efficiency and enhance system safety. Understanding the structure, types, and maintenance of valve manifolds can help maximize their effectiveness in practical applications.
If you have any questions, please contact us directly and we will reach you soon.
